Franche-Comté
 |
 |
From 1956 to 2015, the Franche-Comté was a French administrative region. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Bourgogne-Franche-Comté.
The region is named after the Franche Comté de Bourgogne (Free County of Burgundy), definitively separated from the region of Burgundy proper in the fifteenth century. In 2016, these two-halves of the historic Kingdom of Burgundy were reunited, as the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. It is also the 6th biggest region in France. The name "Franche-Comté" is feminine because the word "comté" in the past was generally feminine, although today it is masculine.
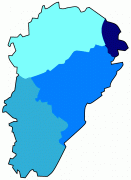
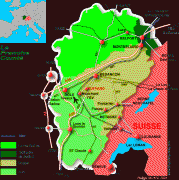
The principal cities are the capital Besançon, Belfort and Montbéliard. Other important cities are Dole (the capital before the region was conquered by Louis XIV in the late seventeenth century), Vesoul (capital of Haute-Saône), Arbois (the "wine capital" of the Jura), and Lons-le-Saunier (the capital of Jura).
The region has been inhabited since the Paleolithic age and was occupied by the Gauls. It was then heavily settled by Germanic peoples during the Germanic migrations, most notably the Burgundians, who settled in the region after the Gauls had vacated the area. Later, it was part of the territory of the Alemanni in the fifth century, then the Kingdom of Burgundy from 457 to 534. The Burgundians adopted Orthodox Christianity, Christianizing the region. In 534, it became part of the Frankish kingdom. In 561 it was included in the Merovingian Kingdom of Burgundy under Guntram, the third son of Clotaire I. In 613, Clotaire II reunited the Frankish Kingdom under his rule, and the region remained a part of the Kingdom of Burgundy under the later Merovingians and Carolingians.
Map - Franche-Comté
Map
Country - France
 |
 |
| Flag of France | |
Inhabited since the Palaeolithic era, the territory of Metropolitan France was settled by Celtic tribes known as Gauls during the Iron Age. Rome annexed the area in 51 BC, leading to a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987. In the High Middle Ages, France was a powerful but highly decentralised feudal kingdom. Philip II successfully strengthened royal power and defeated his rivals to double the size of the crown lands; by the end of his reign, France had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. From the mid-14th to the mid-15th century, France was plunged into a series of dynastic conflicts involving England, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, and a distinct French identity emerged as a result. The French Renaissance saw art and culture flourish, conflict with the House of Habsburg, and the establishment of a global colonial empire, which by the 20th century would become the second-largest in the world. The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Huguenots that severely weakened the country. France again emerged as Europe's dominant power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War. Inadequate economic policies, inequitable taxes and frequent wars (notably a defeat in the Seven Years' War and costly involvement in the American War of Independence) left the kingdom in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. This precipitated the French Revolution of 1789, which overthrew the Ancien Régime and produced the Declaration of the Rights of Man, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | Euro | € | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EU | Basque language |
| BR | Breton language |
| CA | Catalan language |
| CO | Corsican language |
| FR | French language |
| OC | Occitan language |