Aruba
 |
 |
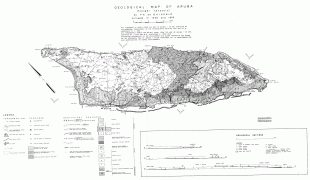
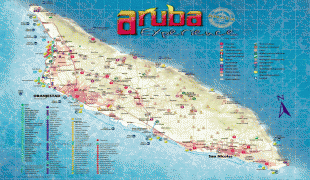
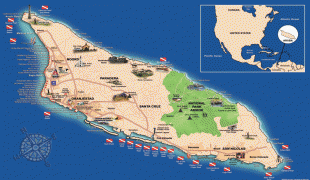
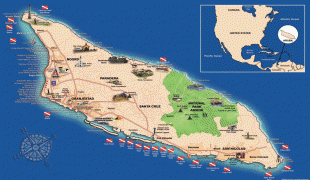
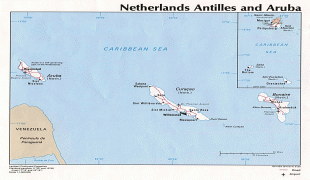
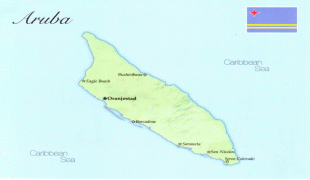
Aruba is one of the four countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands, along with the Netherlands, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten; the citizens of these countries are all Dutch nationals. Aruba has no administrative subdivisions, but, for census purposes, is divided into eight regions. Its capital is Oranjestad. Unlike much of the Caribbean region, Aruba has a dry climate and an arid, cactus-strewn landscape. The relatively warm and sunny weather, and the climate allow for related tourism activities all year round. Its area is 179 km2 and it is quite densely populated, with 108,166 inhabitants per the 2020 census.
The name Aruba most likely came from the Caiquetio Oruba which means "Well situated island", seeing as it was the Caiquetio who were present on the island when it was first set foot upon by Alonso de Ojeda. Between 1529 and the signing of the Treaty of Westphalia (1648), the name "Isla de Oruba" was used for the island by the Spanish. After the signing, the island was ceded to the Dutch and gradually its name changed to Aruba.
There were many different names for Aruba used by other Amerindian groups, all of which could have contributed to the present-day name Aruba. Another Caiquetio name for the island was Oibubia which means "Guided island". The Taino name for the island was Arubeira. The Kalinago also had two names for the island Ora Oubao which means "Shell island" and Oirubae which means "Companion of Curaçao".
A common misconception is that the name "Aruba" came from Oro hubo, (Spanish for "There was gold once"). However, the Spanish declared these islands islas inútiles, meaning "useless islands", due to their lack of mineral wealth. It was not until, a century later, in 1824, that gold was discovered on Aruba by a twelve year-old herder named Willem Rasmijn; leading to the Aruban Gold Rush.